Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are a key component in 3D printing processes. But determining what MOF would be best for a specific application often requires trial and error.
Researchers out of the University of Cambridge have used machine learning techniques to accurately predict the mechanical properties of more than 3,000 existing MOFs, as well as countless MOFs yet to be synthesized in a laboratory.
What Are MOFs?
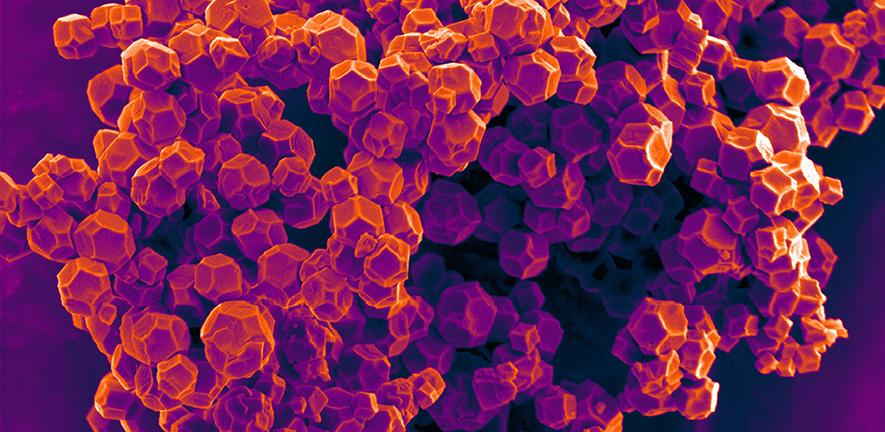
MOFs are self-assembling 3D compounds made of metallic and organic atoms connected together. Like plastics, they are highly versatile, and can be customized into millions of different combinations. Unlike plastics, MOFs have orderly crystalline structures that grow in all directions, which means they can be made like building blocks. Individual atoms or molecules can be switched in or out of the structure, a level of precision that is impossible to achieve with plastics.
Some say MOFs could be as important to 21st century manufacturing as plastics were in the 20th century.
Choosing the Best MOFs for Additive Manufacturing
The structures are highly porous with massive surface area; a MOF the size of a sugar cube laid flat would cover an area the size of six football fields. Somewhat counterintuitively, MOFs also make highly effective storage devices to hold anything from water to dangerous gases. They can also be used in the construction of hydrogen fuel cells. The pores in any given MOF can be customized to form a perfectly shaped storage pocket for different molecules, just by changing the building blocks.
MOFs are synthesized in powder form, but in order to be of any practical use, the powder is put under pressure and formed into larger, shaped pellets. Due to their porosity, many MOFs are crushed in this process, wasting time and money.
To address this problem, researchers developed a machine learning algorithm to predict the mechanical properties of thousands of MOFs, so that only those with the necessary mechanical stability are manufactured.
This advance could allow researchers and developers to determine, in advance, the best material for any given additive manufacturing project.